- Democracy GovernmentDemocracy What is democracy? The word democracy comes from the Greek words “demos“, meaning people, and “kratos” meaning power; so democracy can be thought of… Read more: Democracy Government
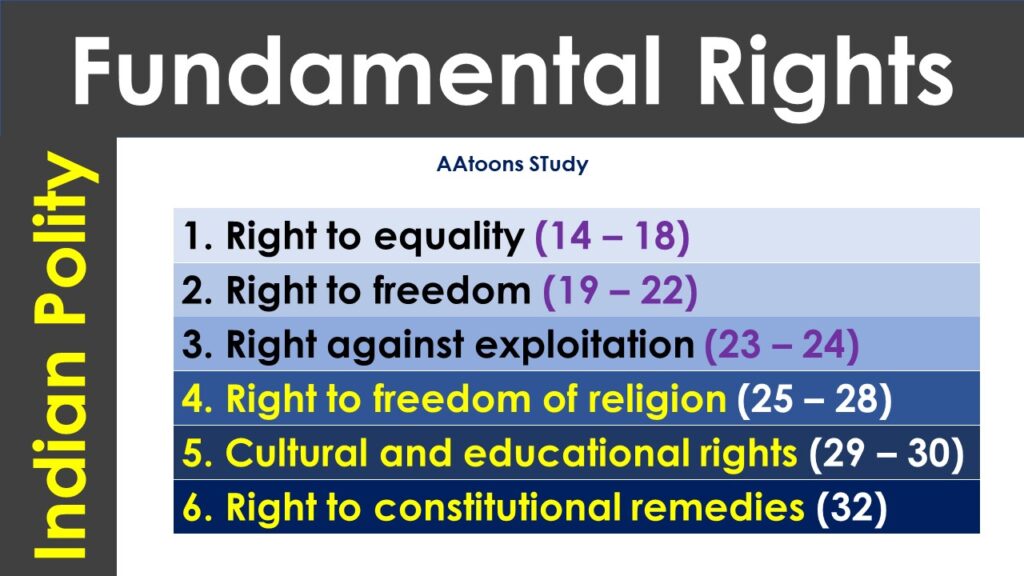
- Fundamental RightsFundamental Rights What is Fundamental Rights? The Fundamental Rights are enshrined in Part III of the Constitution from Articles 12 to 35. Originally, the Constitution… Read more: Fundamental Rights
- Writs of the Indian ConstitutionWrits of the Indian Constitution Writs of the Indian Constitution. B.R. Ambedkar once said that the right to constitutional remedy is known as ‘heart and… Read more: Writs of the Indian Constitution
- All about FIR First Information ReportFIR (First Information Report) FIR stands for First Information Report and FIR is a written document made by the police when someone reports a crime.… Read more: All about FIR First Information Report
- Borrowing features of the Indian ConstitutionBorrowing features of the Indian Constitution 1. Government of India Act of 1935 Federal Scheme, Office of the governor, Judiciary, Public Service Commissions, Emergency provisions… Read more: Borrowing features of the Indian Constitution
- Some Facts About Indian ConstitutionSome Important Facts about Indian Constitution The Indian constitution is unique in its content and spirit. Lengthiest written Constitution Blend of Rigidity and Flexibility Federal… Read more: Some Facts About Indian Constitution
- Making of India ConstitutionIn 1934, an idea for a Constituent Assembly was proposed by Manabendra Nath Roy (M.N. Roy). Note: Narendra Nath Bhattacharya known as Manabendra Nath Roy… Read more: Making of India Constitution
List of all articles
- Democracy Government
- Fundamental Rights
- Writs of the Indian Constitution
- All about FIR First Information Report
- Borrowing features of the Indian Constitution
- Some Facts About Indian Constitution
- Making of India Constitution